The Ultimate Singapore Average Salary Guide | How Much You Should Be Making in 2024

Singapore has some of the highest wages in the world.
According to recent data, Singapore’s median salary for full-time work in Singapore is S$5,170 monthly in 2023, and is projected to be around S$7,310 monthly in 2024, including the employer’s CPF contributions.
But are you underpaid?
What should be the “market salary” for your role?
We’ve put together this Ultimate Singapore Average Salary Guide to help you out. Benchmark your salary against everyone else in your industry.
We’ll talk about different key points of the average salary in Singapore, such as the median salary. We’ll also answer your frequently asked questions about the average salary in Singapore.
So if you’re wondering what a good salary in Singapore is, you’re in the right place. Use this salary information to negotiate a better salary package for yourself. 🙂
In This Guide:
Singapore salary guide: Frequently Asked Questions
- Is there minimum wage in Singapore?
- What’s the difference between gross salary and median salary?
- What’s gross monthly income?
- What’s the average salary in Singapore?
- What are the highest paying jobs in Singapore?
- What are the taxes on salaries in Singapore?
- What are some common benefits usually included in Singaporean salaries?
- What is Singapore’s average salary increment?
- Does education level have a huge impact on salaries in Singapore?
- Where does Singapore’s average salary rank globally?
Singapore’s average salary increases every year, and it can differ depending on specific criteria – permanent residents will see a higher salary than temporary workers, and those in a higher age group will also earn more.
Though we’re going to check out salary numbers and trends for a specific occupation or industry across the before, so let’s jump right ahead!
Is there minimum wage in Singapore?
No, the Singapore Ministry of Manpower does not prescribe minimum wages for all workers in Singapore, local or foreign. The minimum wage law is a little different than most other countries in South East Asia.
But, Singapore does have a scheme called Workfare that supports low wage workers (Singapore citizens) aged 35 and above, who earn a gross monthly income of not more than S$2,300.
What’s the difference between gross salary and median salary in Singapore?
The median salary for a career is the middle point of all salaries for that career.
Simply put, half of the people who work in that field make more than the median salary, and the other half make less than the median salary.
Your gross salary for a month, or monthly gross rate of pay, refers to the amount of money payable for one month’s work.
That includes allowances that you’re entitled to under a contract of service, but excludes
- Additional payments (overtime, bonus, AWS).
- Reimbursement of special expenses incurred during the course of employment.
- Productivity incentive payments.
- Travel, food and housing allowances.
What’s gross monthly income?
Your gross monthly income includes your basic monthly salary, before deduction of employee CPF contributions and personal income tax, plus extra wages such as overtime pay, commissions and bonuses earned.
When people talk about salaries, this gross income is usually the number that they use. So, your gross monthly income refers to total earnings without deductions.
The average salary in Singapore shows an upward trajectory over time.
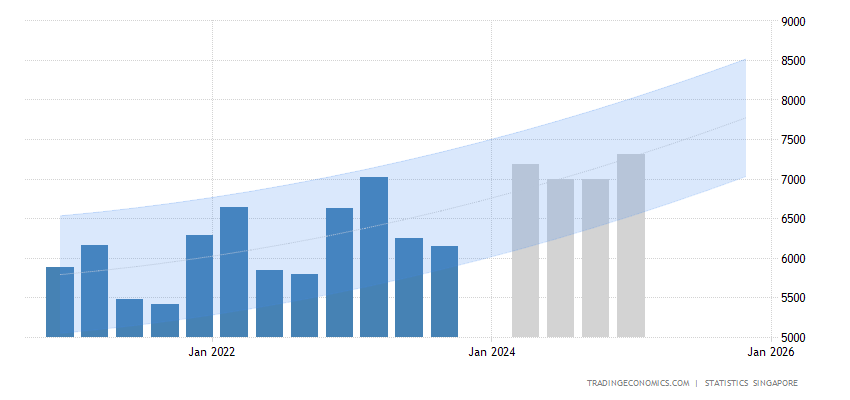
Source: tradingeconomics.com | Statistics Singapore
What’s the average salary in Singapore?
As of 2024, the average salary in Singapore is projected to be around S$7,310 per month.
For full-time employed Singapore residents, the Median Gross Monthly Income from work, including employer CPF contributions, is S$4,563.
It may be better to look at the median gross monthly income, as the median monthly salary is less affected by super-high salaries that bring the average up.
Singapore median salary by age
Figure out how much you should earn according to your age, education, work experience, and industry.
| Age Group | Monthly Median Salary (2022) | Monthly Median Salary (2021) |
| 15 – 19 | S$1,638 | S$1,170 |
| 20 – 24 | S$2,925 | S$2,691 |
| 25 – 29 | S$4,446 | S$4,095 |
| 30 – 34 | S$5,792 | S$5,222 |
| 35 – 39 | S$6,825 | S$6,102 |
| 40 – 44 | S$6,825 | S$6,825 |
| 45 – 49 | S$6,581 | S$5,958 |
| 50 – 54 | S$5,850 | S$5,070 |
| 55 – 59 | S$4,323 | S$3,729 |
| 60 & Over | S$2,621 | S$2,543 |
Source: Labour Force in Singapore
Education
Higher education usually results in a higher base salary, and Singapore is no different.
So let’s examine how your education will impact your average gross salary.
Employees with bachelor’s degrees earn 24% more monthly wages than diploma holders in Singapore.
And professionals with a master’s degree will make 29% more than workers who have finished their bachelor’s degree.
Lastly, Ph.D. holders earn 23% more than those with a master’s degree.
Source: salaryexplorer.com
Work Experience
| Years of Experience | Salary Comparison |
| Below two years (intern or fresh graduates) | Starting salary |
| 2 – 5 years | +32% more than professionals with less than two years of experience |
| 5 – 10 years | +36% more than professionals with 2 – 5 years of experience |
| 10 – 15 years | +21% more than professionals with 5 – 10 years of experience |
| 15 – 20 years | +14% more than professionals with 10 – 15 years of experience |
| +20 years | +9% more than professionals with 15 – 20 of experience |
Source: salaryexplorer.com
What are the highest paying jobs in Singapore?
5% of Singaporeans belong to the world’s richest 1%… WOW. This is in a range of fields, from investment banking through to self employed entrepreneurs.
You might not be there (yet), but it doesn’t hurt to aim high!
Check out our round up of top 5 highest paying jobs for each industry, and let it fuel your career dreams.
What are the taxes on salaries in Singapore?
To put it simply, you need to pay income tax if you earn, derive, or receive income in Singapore unless exempted by the Income Tax Act or an Administrative Concession. If you earn S$22,000 and above, you are required to file your taxes. This includes employees, self-employed individuals, those with investment income, and those working overseas under specific conditions.
According to 2024’s assessment year, Singaporean’s resident tax rates are from 0% to 24%. A personal tax rebate will be granted to all tax residents and will be 50% of tax payable, capped at $200.
Get your full tax breakdown using IRA’s tax calculator.
What are some common benefits usually included in Singaporean salaries?
There are mandatory benefits according to Singapore’s Employment Act; these include annual paid leave, parental/maternity leave, paid sick leave, and worker’s compensation insurance.
Other common benefits companies may provide are yearly bonuses, life and/or health insurance, performance or KPI bonuses, sign-on bonuses, flexible work options, monthly allowances, relocation packages, stock options, education sponsorship, visa sponsorship, and more.
What is Singapore’s average salary increment?
According to Mercer’s Total Remuneration Survey, Singaporean employees may expect a boost of 4.2% in 2024 in median wage. Though it is important to note, that the real growth is forecasted to be 0.5% after a decline in 2023, as shown by the Salary Trends Report by ECA International (ECA).
Does education level have a huge impact on salaries in Singapore?
Although not as important as it used to be, educational level still generally lead to better-paying jobs. A study done by the National University of Singapore (NUS) shows that university graduates are seen to have a wage of 62% higher than the median as compared to those with only a diploma or A-level qualifications.
However, despite higher education levels, all employees in Singapore earn low when young, climb the salary ladder and eventually experience a dip when older.
Where does Singapore’s average salary rank globally?
Singapore currently stands at number 11 globally with a average salary of $4,350 USD (S$5,896).
When comparing salary levels in Singapore to those in other countries, it’s crucial to take into account factors like cost of living, taxation, and social security contributions.
See the table below for the average wages of a few countries as compared to Singapore:
| Country | Median Annual Salary (USD) | Cost of Living Index | Monthly Rent Index |
| Singapore* | 54,530 | 83.12 | 63.27 |
| United States | 65,760 | 71.05 | 40.32 |
| Australia | 54,910 | 72.08 | 36.76 |
| United Kingdom | 42,500 | 67.28 | 36.84 |
| Japan | 38,515 | 83.35 | 25.93 |
| India | 2,100 | 24.58 | 5.68 |
| China | 13,480 | 40.04 | 29.48 |
Average salary in Singapore in 2024, sorted by industry:
Accounting & Finance (Commercial Businesses)
| Job Title | Average Annual Salary (SGD) |
| CFO / VP Finance | $350,000 |
| Tax Director | $250,000 |
| Internal Audit Director | $250,000 |
| Finance Director | $240,000 |
| Treasury Director / Treasurer | $200,000 |
Accounting & Finance (Financial Services)
| Job Title | Average Annual Salary (SGD) |
| CFO (Fund Management) | $350,000 |
| Finance Director | $220,000 |
| Financial Controller | $150,000 |
| Tax (Fund/Asset Management) | $130,000 |
| Product Controller | $120,000 |
| Valuation Control | $120,000 |
| FP&A | $120,000 |
| Performance Analyst (Asset Management) | $120,000 |
| Finance Manager | $120,000 |
Banking Operations
| Job Title | Average Annual Salary (SGD) |
| COO / Head of Operations | $270,000 |
| Trade & Sales Support | $150,000 |
| KYC Operations | $130,000 |
| Client Services | $130,000 |
| Collateral Management | $130,000 |
Compliance
| Job Title | Average Annual Salary (SGD) |
| Sanctions | $200,000 |
| Compliance Testing | $180,000 |
| KYC | $180,000 |
| Transaction Monitoring | $150,000 |
| Regulatory Compliance | $150,000 |
Financial Services (Front Office)
| Job Title | Average Annual Salary (SGD) |
| Managing Director (Investment Banking) | $620,000 |
| Managing Director (Private Banking) | $480,000 |
| Director (Investment Banking) | $450,000 |
| Director (Private Equity) | $400,000 |
| Executive Director (Private Banking) | $350,000 |
HR
| Job Title | Average Annual Salary (SGD) |
| HR Director / Head of HR | $200,000 |
| Head of C&B | $180,000 |
| Head of L&D | $180,000 |
| HR Business Partner | $150,000 |
| C&B Manager | $144,000 |
Marketing
| Job Title | Average Annual Salary (SGD) |
| Vice-President / President / CxO (Technology) | $420,000 |
| Marketing Director / Senior Director (Consumer Goods) | $320,000 |
| Marketing Director / Senior Director (Pharmaceutical & Medical Devices) | $270,000 |
| Regional Head of Marketing / Director / Executive Director (Banking & Financial Services) | $270,000 |
| E-Commerce VP / Director (Digital Marketing) | $270,000 |
Project & Change Management
| Job Title | Average Annual Salary (SGD) |
| Programme Manager | $180,000 |
| Business Transformation | $180,000 |
| Agile Coach | $180,000 |
| Lean Six Sigma / Operational Excellence Expert | $170,000 |
| Business Process Improvement Manager | $170,000 |
Risk Management
| Job Title | Average Annual Salary (SGD) |
| Quant | $150,000 |
| Business Transformation | $180,000 |
| Portfolio Risk & Analytics | $150,000 |
| Enterprise Risk | $140,000 |
| Credit Risk | $130,000 |
| Market Risk | $130,000 |
| Operational Risk | $130,000 |
Sales
| Job Title | Average Annual Salary (SGD) |
| Director / Managing Director | $300,000 |
| Account Director (Regional / Global) | $270,000 |
| Country General Manager / Commercial Director/td> | $220,000 |
| Head of Sales / Business Development Director | $180,000 |
| Head of Strategic Partnerships | $195,000 |
| Category Director | $195,000 |
Supply Chain & Procurement
| Job Title | Average Annual Salary (SGD) |
| Supply Chain Director | $190,000 |
| Procurement / Purchasing Director | $160,000 |
| Supply Chain Manager | $150,000 |
| Procurement / Purchasing Manager | $150,000 |
| Planning Manager | $150,000 |
| Project Manager SCM | $150,000 |
Looking to switch jobs this year? We’ve got your back:
Download one of our free resume templates to use. You don’t have to be a professional resume writer, we have templates for many different industries and roles.
While you’re sprucing up your resume, why not check out our Ultimate CV Guide and Cover Letter Guide?
They’re chock-full of useful tips for an absolutely killer CV and Cover Letter – our tricks of the trade from over a decade of recruitment experience.
And if you need some extra resume help, we’ll even polish up your CV or Cover Letter in no time, just reach out.
Return to Ultimate Singapore Job Search Hub
Sources: Morgan McKinley, Ministry of Manpower
- Top 10 Digital Marketing Courses in Singapore 2024 - October 17, 2024
- Top 10 Practical SkillsFuture Courses to Spend Your SkillsFuture Credits On - October 14, 2024
- What Is Sabbatical Leave? | How It Works in Singapore - September 1, 2024